NURS 6521 Week 3 EmmaGarcia Asthma and Stepwise Management Sample Solution Included Asthma and Stepwise Management Sample Presentation Notes
Slide 1 – Introduction
Welcome to this staff education session on Asthma Management.
This presentation aims to provide valuable insights into understanding and effectively managing asthma in patients.
Healthcare professionals can enhance patient outcomes and the standard of care by improving their knowledge and expertise in managing asthma.
This presentation will explore key concepts, treatment options, and stepwise approaches that empower healthcare providers to deliver optimal care for patients with asthma.
Slide 2 – Long-Term Control Treatment Options for Asthma
In asthma management, various medications play vital roles in achieving long-term control of the disease. Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) are the cornerstone of long-term control as they effectively reduce airway inflammation, a key component of asthma. These medications help prevent and manage asthma symptoms by reducing inflammation and improving overall lung function. Long-acting beta-agonists (LABAs) are often used in combination with ICS. They work by relaxing the airway muscles, resulting in bronchodilation and improved airflow (Rosenthal & Burchum, 2021). LABAs provide sustained relief and help control symptoms for an extended period.
Leukotriene modifiers are another class of medications used in asthma management. They block the chemicals responsible for inflammation and constriction of the airways, helping to prevent asthma symptoms. Immunomodulators are medications that modify the immune response to prevent asthma symptoms. They target specific components of the immune system involved in the inflammatory process, thereby reducing the frequency and severity of asthma attacks.
Mast cell stabilizers are used to prevent the release of asthma-triggering chemicals from mast cells (Rosenthal & Burchum, 2021). By stabilizing these cells, mast cell stabilizers help reduce airway inflammation and prevent the onset of asthma symptoms. For severe asthma cases, monoclonal antibodies are utilized. These medications target specific immune molecules involved in the inflammatory cascade of asthma. Monoclonal antibodies help control severe asthma symptoms and reduce the frequency of exacerbations, offering a targeted approach to treatment (Rosenthal & Burchum, 2021).
Slide 3 – Quick Relief Treatment Options for Asthma
Short-acting beta-agonists (SABAs) are crucial in asthma management as they provide quick relief during acute symptoms by rapidly relaxing the airway muscles and promoting bronchodilation. They are commonly used as rescue medications to alleviate sudden asthma attacks. Anticholinergics, often used in combination with SABAs, help relax the airway muscles further and improve bronchodilation (Rosenthal & Burchum, 2021). By blocking the action of acetylcholine, these medications reduce airway constriction and improve airflow.
Systemic corticosteroids play a vital role in controlling severe asthma exacerbations. These medications, typically prescribed for short periods, effectively reduce airway inflammation, improve lung function, and help manage acute episodes of asthma. Beta-agonist tablets are reserved for specific cases where immediate relief is required. They provide rapid bronchodilation and are typically used when other forms of medication or inhalers are not accessible or do not offer sufficient relief. Rescue inhalers, containing short-acting bronchodilators, offer a portable and convenient option for immediate symptom relief (Rosenthal & Burchum, 2021). They are designed to be used on the go and provide quick relief by delivering medication directly to the airways.
A personalized asthma action plan is an essential tool that empowers patients to manage their symptoms and treatment effectively. It provides clear instructions on medication usage, trigger avoidance, and steps to take during worsening symptoms or exacerbations (Rosenthal & Burchum, 2021). The asthma action plan helps patients recognize early warning signs, take appropriate actions, and maintain control over their condition.
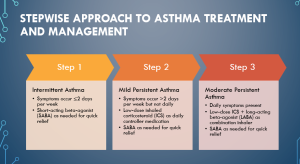
Slide 4 – Stepwise Approach to Asthma Treatment and Management
The stepwise approach to asthma treatment and management provides a structured framework for healthcare providers to tailor treatment based on the severity and frequency of symptoms experienced by patients.
Step 1 – Intermittent Asthma: At this stage, symptoms occur infrequently, with episodes happening two or fewer days per w