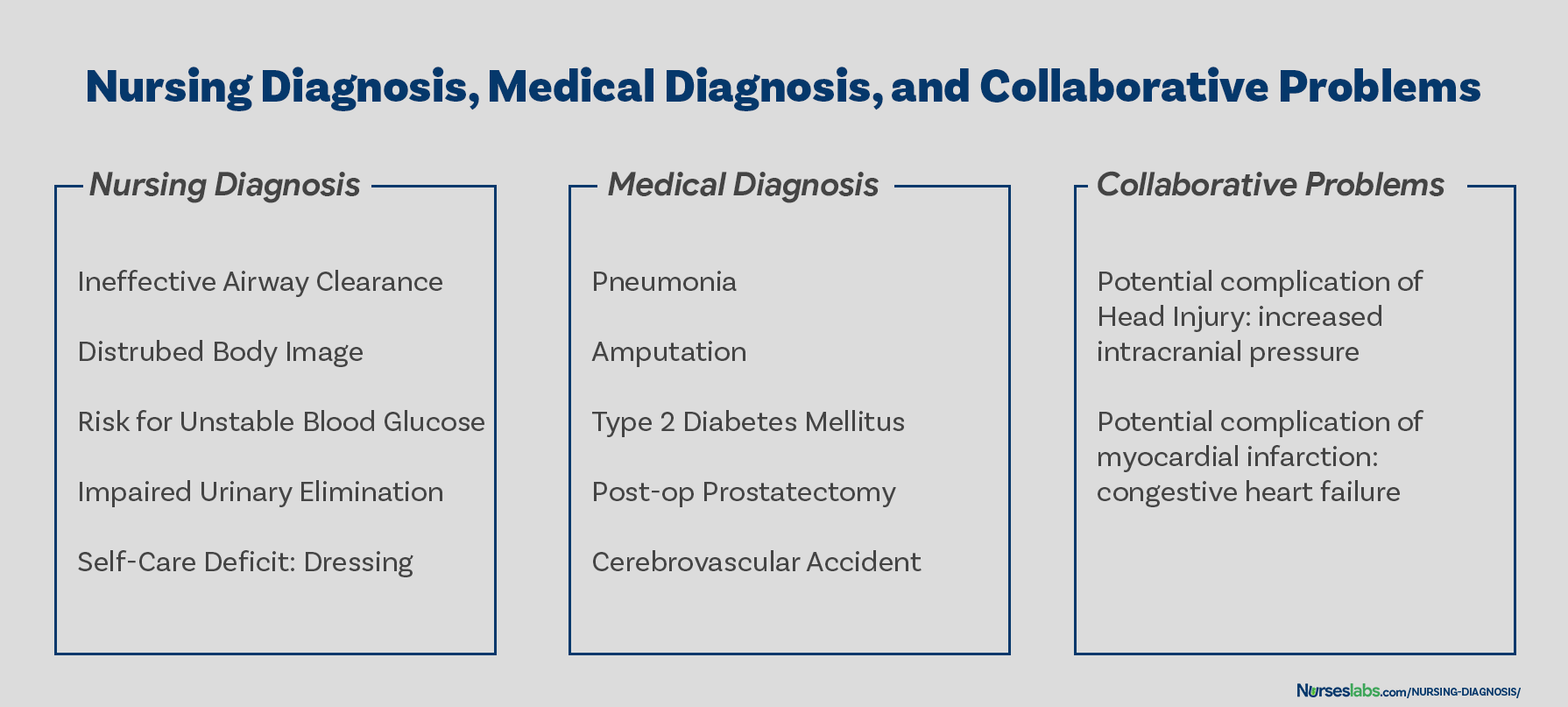
Differentiating Nursing Diagnoses, Medical Diagnoses, and Collaborative Problems
Purposes of Nursing Diagnosis
The purpose of the nursing diagnosis is as follows:- For nursing students, nursing diagnoses are an effective teaching tool to help sharpen their problem-solving and critical thinking skills.
- Helps identify nursing priorities and helps direct nursing interventions based on identified priorities.
- Helps the formulation of expected outcomes for quality assurance requirements of third-party payers.
- Nursing diagnoses help identify how a client or group responds to actual or potential health and life processes and knowing their available resources of strengths that can be drawn upon to prevent or resolve problems.
- Provides a common language and forms a basis for communication and understanding between nursing professionals and the healthcare team.
- Provides a basis of evaluation to determine if nursing care was beneficial to the client and cost-effective.
Differentiating Nursing Diagnoses, Medical Diagnoses, and Collaborative Problems
The term nursing diagnosis is associated with different concepts. It may refer to the distinct second step in the nursing process, diagnosis (“D” in “ADPIE“). Also, nursing diagnosis applies to the label when nurses assign meaning to collected data appropriately labeled a nursing diagnosis. For example, during the assessment, the nurse may recognize that the client feels anxious, fearful, and finds it difficult to sleep. Those problems are labeled with nursing diagnoses: respectively, Anxiety, Fear, and Disturbed Sleep Pattern. In this context, a nursing diagnosis is based upon the patient’s response to the medical condition. It is called a ‘nursing diagnosis’ because these are matters that hold a distinct and precise action associated with what nurses have the autonomy to take action about with a specific disease or condition. This includes anything that is a physical, mental, and spiritual type of response. Hence, a nursing diagnosis is focused on care.Order Now