Diagnostic Process: How to Diagnose
There are three phases during the diagnostic process: (1) data analysis, (2) identification of the client’s health problems, health risks, and strengths, and (3) formulation of diagnostic statements.
Analyzing Data
Analysis of data involves comparing patient data against standards, clustering the cues, and identifying gaps and inconsistencies.Identifying Health Problems, Risks, and Strengths
In this decision-making step, after data analysis, the nurse and the client identify problems that support tentative actual, risk, and possible diagnoses. It involves determining whether a problem is a nursing diagnosis, medical diagnosis, or a collaborative problem. Also, at this stage, the nurse and the client identify the client’s strengths, resources, and abilities to cope.Formulating Diagnostic Statements
Formulation of diagnostic statements is the last step of the diagnostic process wherein the nurse creates diagnostic statements. The process is detailed below.How to Write a Nursing Diagnosis?
In writing nursing diagnostic statements, describe an individual’s health status and the factors that have contributed to the status. You do not need to include all types of diagnostic indicators. Writing diagnostic statements vary per type of nursing diagnosis (see below).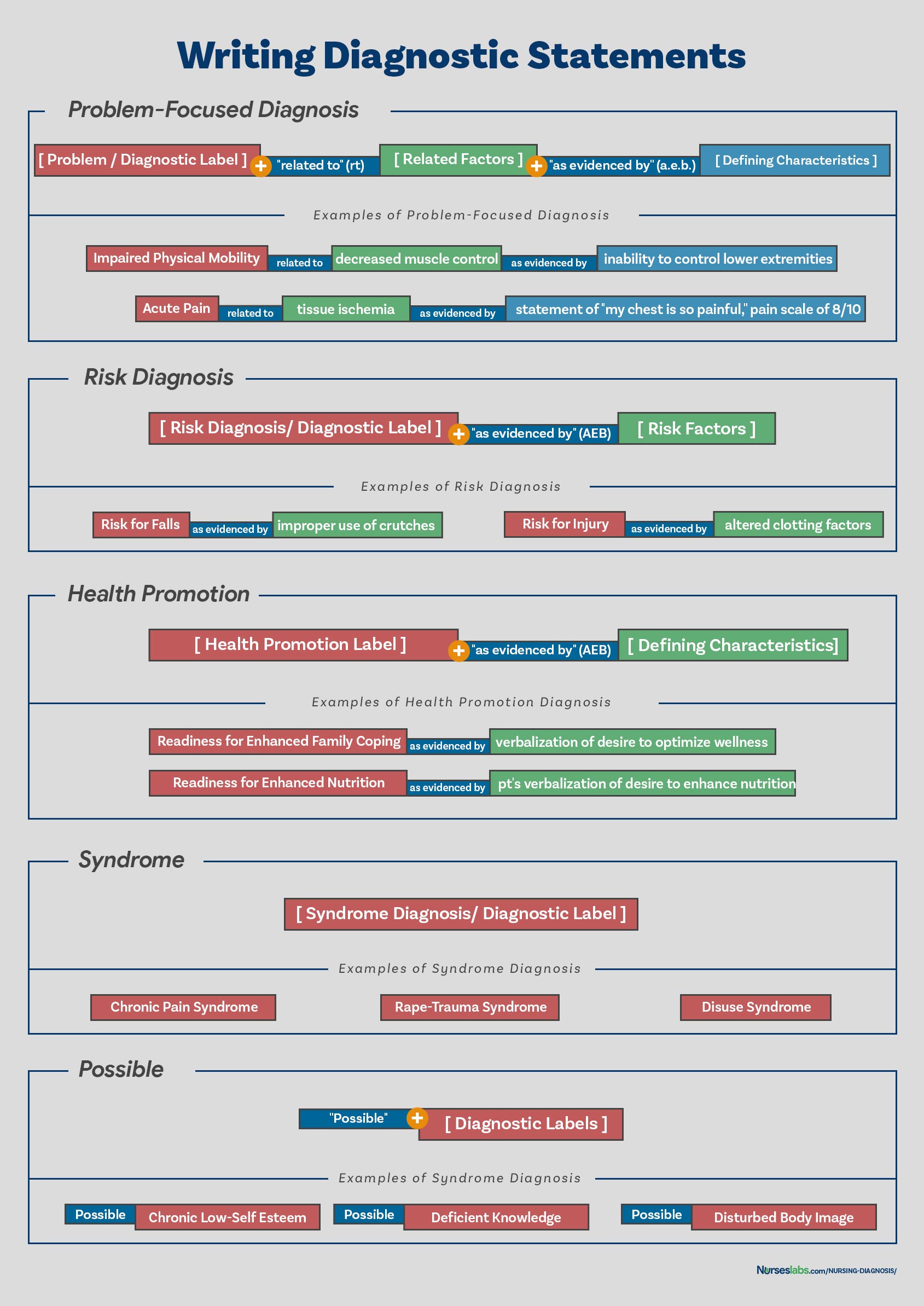
PES Format
Another way of writing nursing diagnostic statements is by using the PES format, which stands for Problem (diagnostic label), Etiology (related factors), and Signs/Symptoms (defining characteristics). Diagnostic statements can be one-part, two-part, or three-part using the PES format.
Order Now